|
GT RoboCup SSL
Soccer software, robot firmware
|
 |
GT RoboCup SSL
Soccer software, robot firmware
|
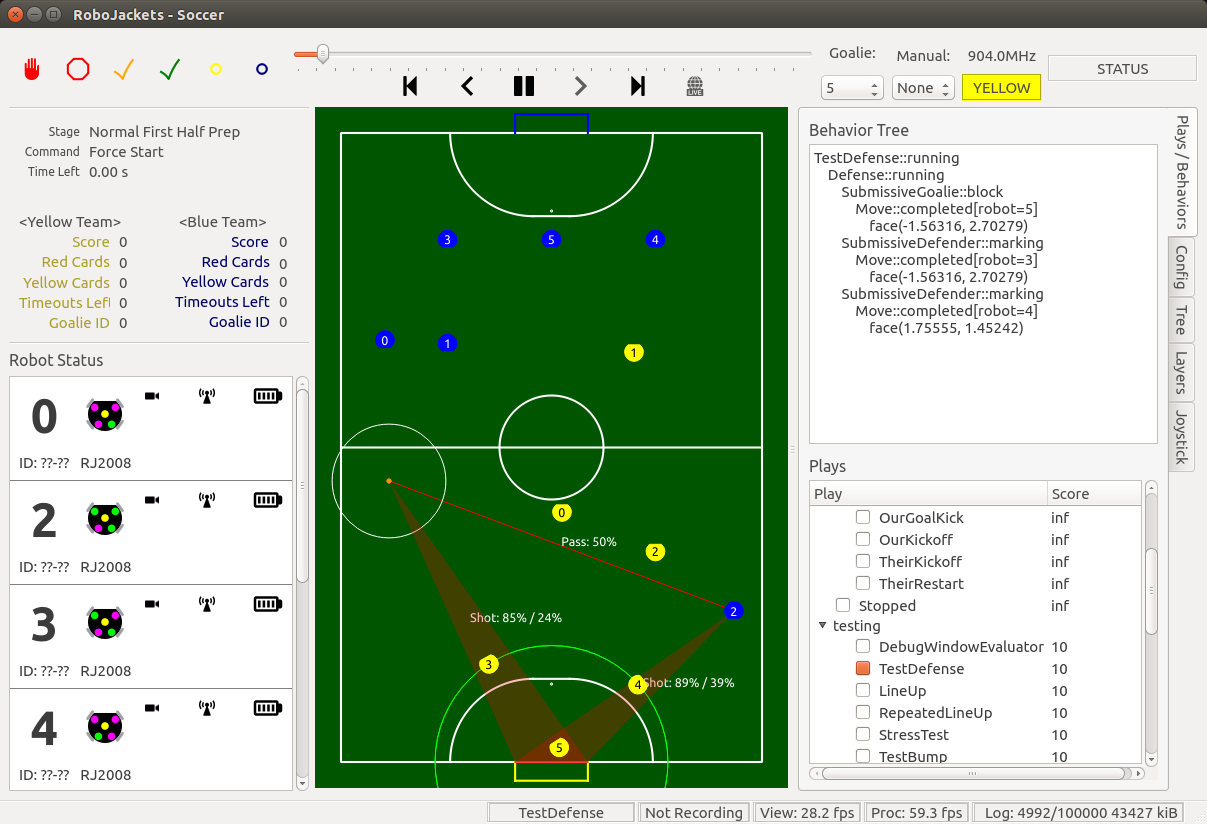
The 'soccer' program is responsible for receiving data from the vision and referee computers and using the information to strategically command the robots on the field (or in the simulator).
Start both soccer and the simulator from the terminal:
In the simulator, you can move the robots and ball around by clicking and dragging. The ball can also be given a velocity by right-clicking and dragging on it.
Start soccer:
Also, make sure that the cameras and vision system are on. If so, robots should show up within the soccer window at their correct locations.
To run without using the AI/vision system, click the 'Manual' dropdown in the upper right of soccer and select the shell number of the robot you want to control with the joystick.
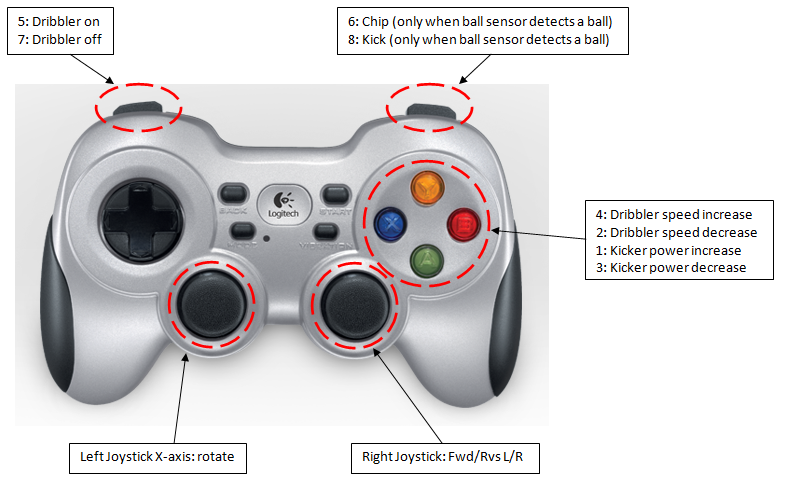
Here's a diagram of the button layout for gamepad joystick control:
In addition to the Logitech Gamepad joystick, you can also use the SpaceNavigator 3d mouse. In order to do so, you have to have the spacenavd userspace driver daemon running. Do this with:
You can also use the systemd service file included with the libspnav source to have spacenavd run at bootup.
See the docs for SpaceNavJoystick for more info and button layouts.
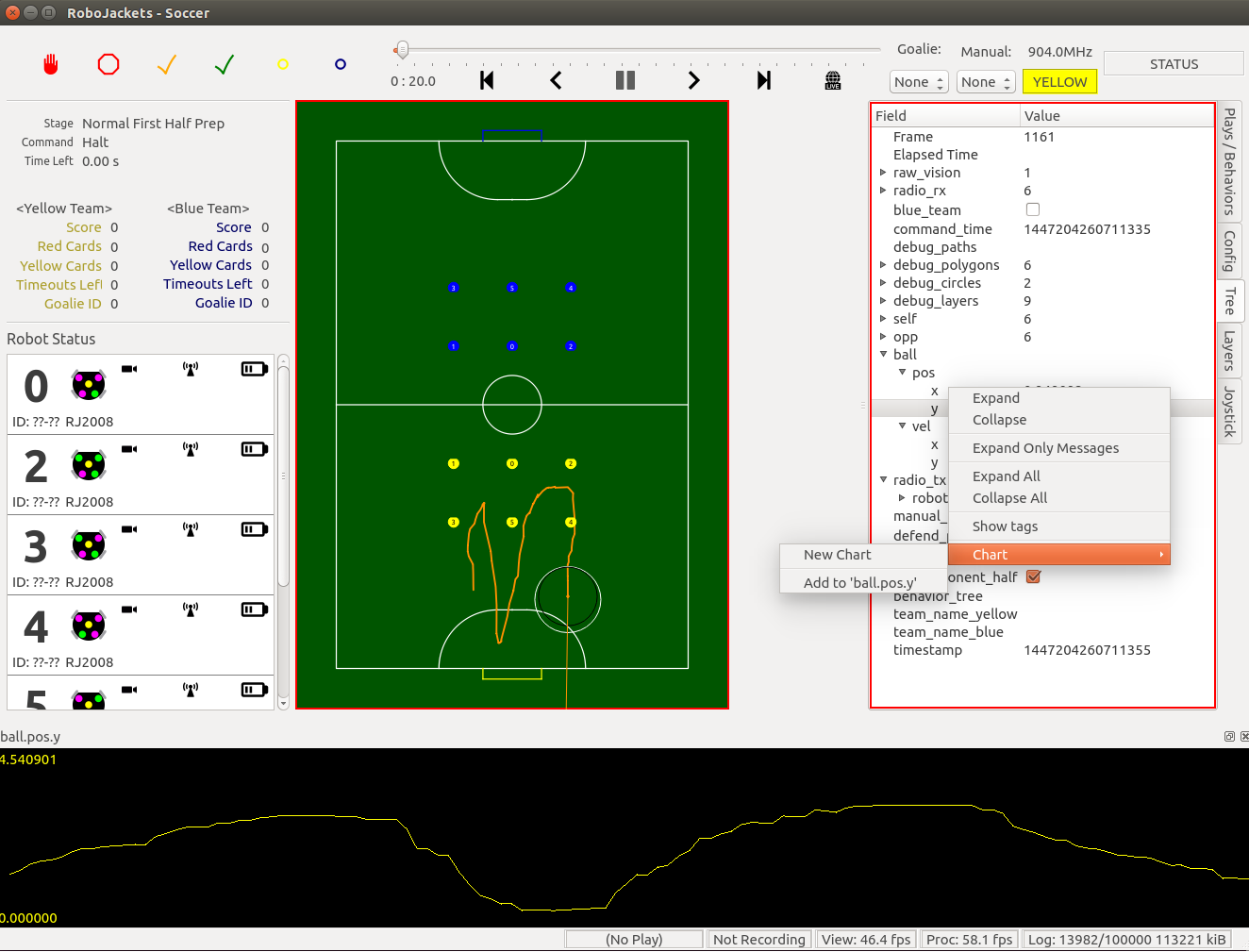
The soccer program has a feature that allows graphing any of the numeric values in the 'Tree' tab. Simply right-click on a value field, then click 'New Chart' or 'Add to ____' and a graph view will be shown at the bottom of the window.